Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunctions
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunctions are disorders that affect the jaw joint and the muscles controlling jaw movement. These conditions can cause pain, discomfort, and a range of other symptoms that impact daily life. Understanding TMJ dysfunctions, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help manage this condition effectively and improve quality of life.
The temporomandibular joint acts as a sliding hinge, connecting the jawbone to the skull. TMJ dysfunctions occur when there are problems with the muscles and joints that control jaw movement. This can result from a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, or jaw misalignment.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to TMJ dysfunctions, including:
- Injury: Trauma to the jaw or head can damage the TMJ. This damage can disrupt the normal function of the joint, leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Arthritis: Conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the TMJ. These inflammatory conditions can cause joint deterioration and inflammation, resulting in pain and restricted movement.
- Jaw Misalignment: Misalignment of the teeth or jaw can lead to TMJ issues. When the teeth do not align properly, it can cause uneven pressure on the TMJ, leading to dysfunction and discomfort.
- Bruxism: Chronic teeth grinding or clenching can strain the TMJ. This repetitive motion places excessive stress on the joint and surrounding muscles, often resulting in pain and inflammation.
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to muscle tension and exacerbate TMJ problems. Stress-induced behaviors, such as clenching the jaw or grinding teeth, can contribute to the development and persistence of TMJ dysfunctions.
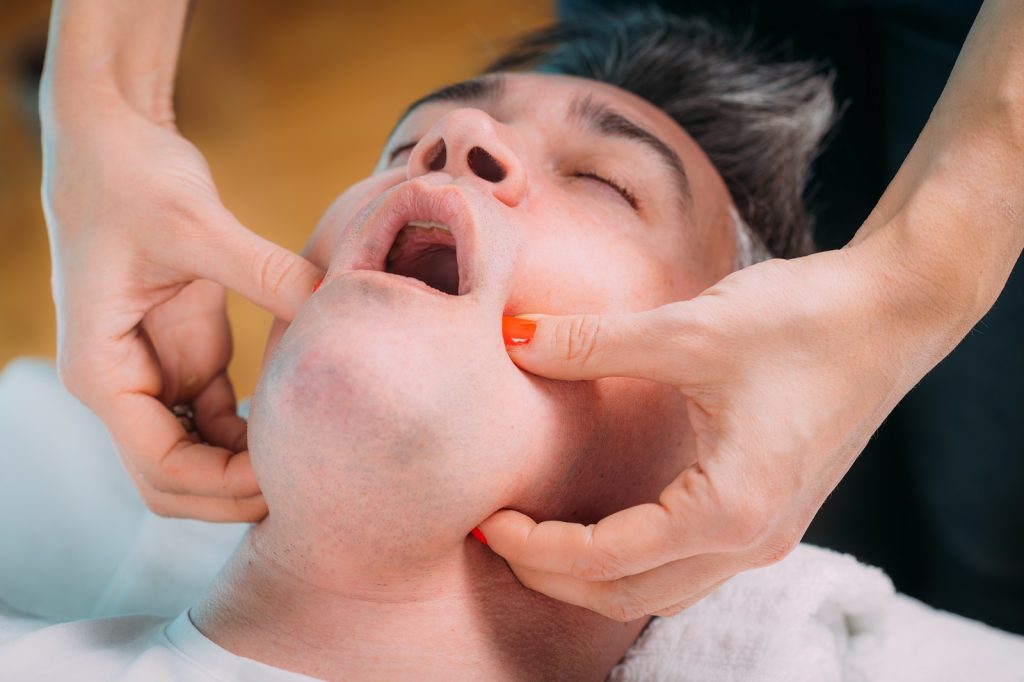
Symptoms
TMJ dysfunctions can present a variety of symptoms, which may vary in severity:
- Jaw Pain: Pain or tenderness in the jaw, particularly around the joint area. This pain can be constant or occur during activities such as chewing or speaking.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches or migraines, often concentrated around the temples or the base of the skull. These headaches can be severe and persistent, impacting daily activities.
- Ear Pain: Pain in or around the ears, which can sometimes be mistaken for ear infections. This pain is often due to the proximity of the TMJ to the ear canal.
- Clicking or Popping: Noises when opening or closing the mouth. These sounds are caused by the displacement of the TMJ disc or irregular movement of the joint.
- Difficulty Chewing: Discomfort or difficulty when chewing or biting. This symptom can make eating challenging and may lead to dietary changes.
- Lockjaw: Inability to fully open or close the mouth. Lockjaw can be temporary or chronic, significantly limiting jaw movement.
- Facial Pain: Pain in the face, neck, or shoulders. This pain is often due to muscle strain and can extend beyond the immediate area of the TMJ.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing TMJ dysfunctions typically involves a combination of physical examinations, patient history, and imaging tests:
- Physical Examination: During a physical exam, the healthcare provider will assess jaw movement, palpate the joint and surrounding muscles to identify pain points, and listen for joint sounds such as clicking or popping. This examination helps determine the presence and extent of TMJ dysfunction.
- Patient History: Gathering a detailed medical history is crucial. The healthcare provider will ask about symptoms, their duration, and potential triggers or contributing factors, such as stress, teeth grinding, or recent injuries.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are used to view the joint structure and identify any abnormalities. X-rays can reveal bone abnormalities, while MRI and CT scans provide detailed images of the soft tissues, including the TMJ disc and surrounding muscles, to detect inflammation, damage, or misalignment.
Treatment Options
Managing TMJ dysfunctions often requires a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and sometimes surgical interventions:
- Medications: Various medications can help manage pain and inflammation associated with TMJ dysfunctions. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are commonly used. For more severe pain, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants or stronger pain medications.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises aimed at strengthening jaw muscles and improving mobility can be highly effective. Physical therapy may include stretching, strengthening exercises, and techniques to improve posture and reduce jaw tension.
- Lifestyle Changes: Implementing stress reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises, can help alleviate TMJ symptoms. Avoiding hard or chewy foods that strain the jaw, practicing good posture, and maintaining a healthy diet can also be beneficial.
- Dental Treatments: Custom-made mouthguards or splints can prevent teeth grinding (bruxism) and correct bite issues. These dental devices help to reduce pressure on the TMJ and alleviate associated pain.
- Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections can be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the TMJ. Botox injections may also be considered to relax muscles and alleviate tension.
- Surgical Options: For severe cases of TMJ dysfunction that do not respond to other treatments, surgical interventions might be necessary. Procedures such as arthrocentesis (joint flushing), arthroscopy (minimally invasive joint surgery), or open-joint surgery can help repair or replace the damaged joint.
Prevention Tips
Preventing TMJ dysfunctions involves adopting healthy habits and being mindful of factors that can contribute to jaw strain:
- Avoid Hard Foods: Minimize the intake of hard or chewy foods that can strain the jaw.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-relief activities such as yoga, meditation, and relaxation techniques.
- Good Posture: Maintain proper posture, especially when sitting for long periods.
- Jaw Exercises: Regularly perform gentle jaw exercises to maintain joint flexibility.
TMJ dysfunctions can be painful and disruptive, but with the right approach, symptoms can be managed effectively. If you experience persistent jaw pain, headaches, or other symptoms associated with TMJ dysfunctions, it is important to seek medical advice.
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule a consultation with Dr. Burhan, please contact us today. Our team of specialists is dedicated to diagnosing and treating TMJ dysfunctions with personalized care plans tailored to your specific needs. We are here to help you find relief from pain and improve your jaw function. Don’t let TMJ dysfunctions disrupt your life—get in touch with us now to start your journey to recovery.


