Acute and Chronic Neck Pain
Neck pain is a common complaint that can range from a mild discomfort to severe pain, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. It can be classified into two main categories: acute and chronic. Understanding the differences between these types, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help in managing and alleviating neck pain effectively.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of acute neck pain:
- Muscle Strain: Overuse or sudden movements of the neck muscles can lead to strain and subsequent pain. Activities such as heavy lifting, sudden jerking movements, or poor posture while sitting can strain the muscles of the neck.
- Injury: Trauma from accidents, such as whiplash from a car accident or a fall, can cause acute neck pain. The sudden force exerted on the neck during impact can result in soft tissue injuries, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Poor Posture: Prolonged periods of sitting or standing in a poor posture, such as slouching while working at a computer or looking down at a phone, can strain the muscles and ligaments of the neck, causing pain and stiffness.
- Sleeping Positions: Using an inadequate pillow or sleeping in an awkward position can place strain on the neck muscles and joints, leading to discomfort upon waking.
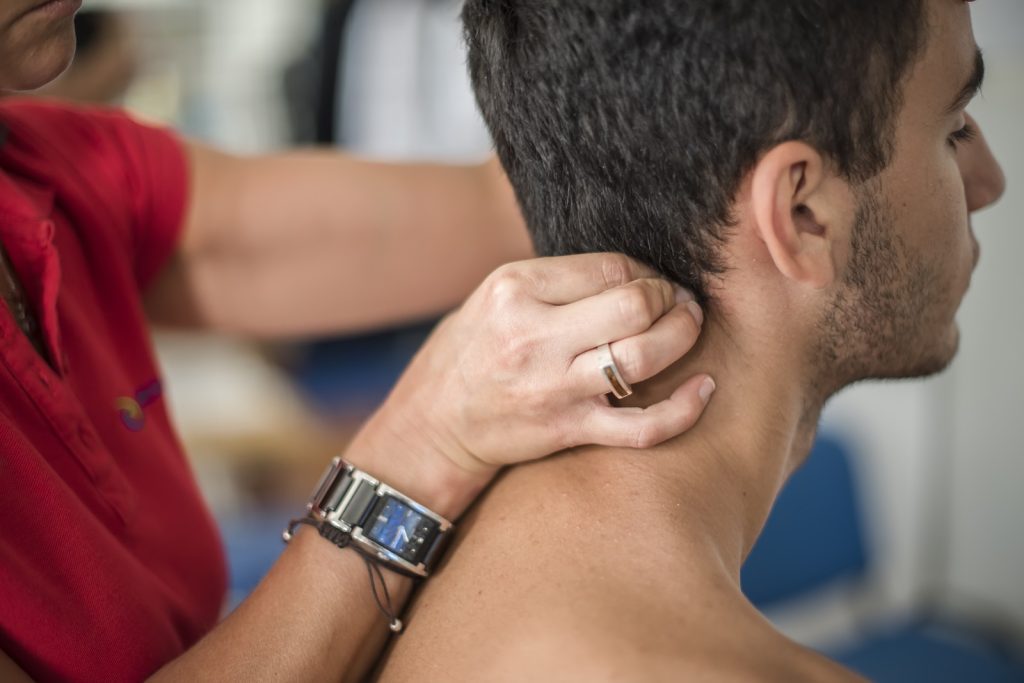
Acute Neck Pain
Acute neck pain refers to sudden-onset pain that typically lasts for a short period, usually less than six weeks. It can be triggered by various factors and often resolves on its own with appropriate treatment and management. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for acute neck pain is essential for effective management and relief.
Symptoms
The symptoms of acute neck pain can vary in severity and may include:
- Sharp Pain: Sudden, intense pain that may worsen with movement or certain activities.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the neck due to muscle tightness and discomfort.
- Headaches: Pain that radiates from the neck to the head, often resulting in headaches.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty turning the head or bending the neck due to pain and stiffness.
Treatment Options
Treatment for acute neck pain aims to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Common treatment options include:
- Rest: Taking a break from activities that strain the neck, such as heavy lifting or repetitive movements, allows the muscles to relax and heal.
- Ice/Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs or heat packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and soothe sore muscles. Ice is typically recommended during the first 48 hours after injury, followed by heat therapy to promote blood flow and relaxation.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the neck. Physical therapy may also include manual therapy techniques to relieve muscle tension and improve posture.
- Proper Ergonomics: Adjusting workstations and improving posture while sitting or standing can help prevent strain on the neck muscles and reduce the risk of future injuries.
Chronic Neck Pain
Chronic neck pain is characterized by persistent pain that lasts for longer than three months. It can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, often resulting from underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for chronic neck pain is crucial for effectively managing this condition.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of chronic neck pain:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related wear and tear on spinal discs can lead to degeneration and chronic pain in the neck. As the discs lose hydration and elasticity, they become more susceptible to injury and inflammation.
- Cervical Spondylosis: Also known as neck arthritis, cervical spondylosis occurs when the cartilage and bones in the neck deteriorate over time, leading to chronic pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility.
- Herniated Disc: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner core of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, pressing on nearby nerves and causing chronic pain, numbness, and weakness in the neck and arms.
- Chronic Strain: Prolonged poor posture, repetitive movements, or activities that place strain on the neck muscles and ligaments can lead to chronic pain and discomfort over time.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tender points throughout the body, including the neck.
Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic neck pain can vary in severity and may include:
- Persistent Pain: Ongoing pain that may fluctuate in intensity but persists for longer than three months.
- Numbness/Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling in the arms or hands, often due to nerve compression in the neck.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the neck, shoulders, or arms, which can affect daily activities and mobility.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that spreads from the neck to the shoulders, arms, or back, often following the path of affected nerves.
- Sleep Disturbances: Pain that interferes with sleep, leading to fatigue and decreased quality of life.
Treatment Options
Treatment for chronic neck pain aims to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and address underlying causes. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Prescription pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques can help strengthen neck muscles, improve posture, and reduce pain.
- Chiropractic Care: Manual adjustments by a chiropractor can help realign the spine, alleviate pressure on nerves, and improve neck function.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical interventions such as discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion may be considered to address structural issues in the neck.
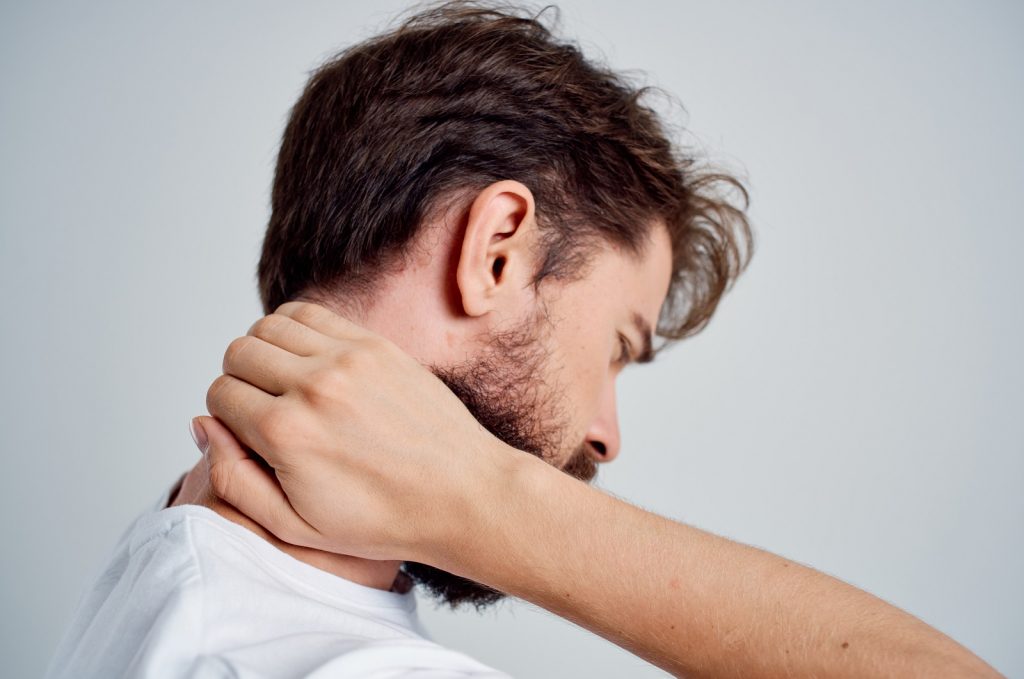

Both acute and chronic neck pain can significantly impact daily life, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can lead to effective management and relief. If you are experiencing persistent neck pain, it is important to seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule a consultation with Dr. Burhan, please contact us today. Our dedicated team of professionals is ready to provide personalized care and effective solutions for managing your neck pain. Whether you are experiencing acute or chronic symptoms, we are here to help you find relief and improve your quality of life. Don’t let neck pain hold you back—get in touch with us now to start your journey to recovery.


